Payouts
At any time you can pay out funds from you Virtual Account to an external account.
Initiating Payout
You can initiate Payout in the following way:
- From Merchant Portal, Balances section
- Using Volume API
Initiating Payout in Merchant Portal
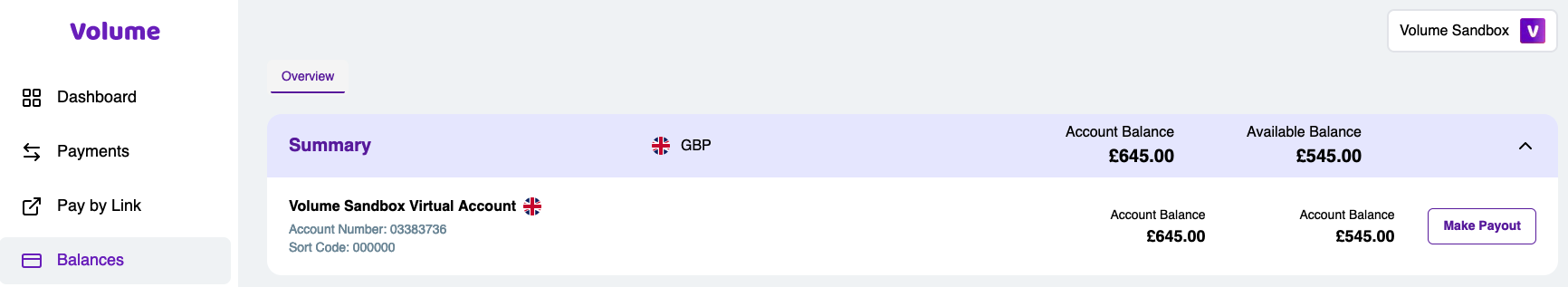
In order to make a Payout, please go to Balances section and press Make Payout next to the account you want to make payment from.


Once you've made the payment and it has been finished, you'll see change in balance reflected in the same Balances page.
Payout status
Payout status is delivered to you by Payout Webhooks.
Payout status has following values:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| IN_PROGRESS | payment is in progress |
| PROCESSED | payment is was processed (does not mean delivered) |
| CANCELLED | payment was cancelled |
| FAILED | payment failed |
| HELD | payment is held and may require contact with volume for it's further processing |
| RETURNED | payment was delivered to destination account and returned |
Payout status delivered by Webhooks
Once you've configured Payout Webhook URL in Merchant Portal, in Settings->Webhooks And Callbacks section, you will be provided with a Webhook for any status change.
Delivery guarantee
Each webhook is delivered until your endpoint answers with 200 OK.
Body
Webhook calls will be delivered as PUT REST call with following payload
{
"eventTimeUtc" : "2024-11-07T07:55:27.004128Z",
"applicationId" : "62b36790-f8cd-4764-8e19-2e19ada49cb1",
"payoutId" : "50cb26b8-1a2d-4455-ba2a-f1c229779500",
"payoutAmount" : 0.30,
"payoutCurrency" : "GBP",
"payoutReference" : "241107073325914PYB",
"payoutStatus" : "IN_PROGRESS",
"payoutStatusDescription" : "",
"payoutWebhookDeliveryAttempt" : 0,
"destination" : {
"type" : "SCAN",
"name" : "John Smith",
"accountNumber" : "12345678",
"sortCode" : "123456"
}
}Important headers
Expect this call with following headers:
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | application/json |
| Accept | application/json |
| Authorization | signature of the request calculated as described here |
Security
You can verify webhook integrity by checking it's signature passed via Authorization header. Mechanism is identical to signature verification if regular payment webhooks. You can find description here
Initiating Payout using Volume API
You can also initiate a Payout using Volume's API.
Please contact your Customer Success Manager or send us an email at support@getvolume.com to request access to this feature.
Prerequisites
In order to initiate a payout via the API, you would need to obtain the details below:
- Application ID - can be found in your Merchant Portal -> Settings -> Security (opens in a new tab) -> Application ID.
- Application Secret - If you don't have it already, you can generate it in Merchant Portal -> Settings -> Security (opens in a new tab) -> Primary private key -> Reset.
- payInAccountSelector - Reach out to support@getvolume.com to obtain your pay-in selector ID.
- Enabled Payout API feature - In order to intiaite a payout via API a particualr feature flag has to be enabled. Reach out to your Customer Success Manager or support@getvolume.com to enable this feature.
Overview
This document describes the algorithm for signing HTTP requests to the Volume API using RFC 9421 HTTP Message Signatures with Ed25519 cryptographic signatures.
All API requests must include a valid signature to prove:
- Authenticity: The request comes from the holder of the private key
- Integrity: The request has not been modified in transit
- Freshness: The request was created recently (not a replay attack)
Requirements
Cryptographic Algorithm
- Signature Algorithm: Ed25519 (EdDSA with Curve25519)
- Hash Algorithm: SHA-512 (for content digest only)
Credentials
- Private Key: 32-byte Ed25519 private key (seed), base64-encoded
- Key ID: Unique identifier for your key pair (provided by Volume)
- Application ID: Your merchant application identifier (REQUIRED)
HTTP Headers
For requests WITH body (POST, PUT, PATCH):
Signature-Input: Metadata about the signatureSignature: The cryptographic signature (base64-encoded)Content-Digest: SHA-512 hash of the request body
For requests WITHOUT body (GET, DELETE):
Signature-Input: Metadata about the signatureSignature: The cryptographic signature (base64-encoded)- NO
Content-Digestheader (butcontent-digeststill included in signature base with empty value)
Algorithm Steps
Step 1: Calculate Content Digest (RFC 9530)
If the request has a body (POST, PUT, PATCH), calculate its SHA-512 digest:
1. Compute SHA-512 hash of the request body bytes
2. Encode the hash as base64
3. Format as: "sha-512=:" + base64Hash + ":"
4. Add to headers: Content-Digest: sha-512=:base64Hash:⚠️ CRITICAL: The request body used to calculate the digest MUST be byte-for-byte identical to the body you actually send in the HTTP request. Even a single extra space, newline character, or difference in JSON formatting will cause signature verification to fail. The body serialization must be exactly the same.
Example:
Body: {"applicationId":"merchant-app-123","payInAccountSelector":"687","amount":10,"reference":"Reference123","destination":{"destinationType":"toAccount","accountType":"SCAN","holderName":"John Doe","accountNumber":"11111111","sortCode":"111111","iban":null}}
SHA-512 (hex): 0507A2CE5DB3677CA6E374BF17FEFACDBCD323D9C71F9972380B1026FCE0273D83A24355BDDCA169ADB48DC333129A597FE846D7FB65CD27E752B2409DB0A009
Base64: BQeizl2zZ3ym43S/F/76zbzTI9nHH5lyOAsQJvzgJz2DokNVvdyhaa20jcMzEppZf+hG1/tlzSfnUrJAnbCgCQ==
Header: Content-Digest: sha-512=:PI9dqqYUxgm7Q8I7IXNvTWddWlhAeQB9iNcVyYWDK0rDrAQDMKfOogMODla92gYbxeKHYUEbCgSb20ah/Yt2hQ==:Empty Body: For GET, DELETE, or requests with no body:
- Do NOT add the
Content-Digestheader to the HTTP request - BUT you MUST still include
content-digestas a component in the signature base with an empty value (nothing after colon+space) - This ensures consistent signature structure across all request types
Step 2: Build the Signature Base from Your HTTP Request
Your HTTP Request Example
Let's start with a concrete request you want to sign:
POST /api/payouts HTTP/1.1
Host: api.volume.com
Content-Type: application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
Content-Length: 40
X-Application-Id: merchant-app-123
X-Application-Secret: merchant-app-secret123
{"applicationId":"merchant-app-123","payInAccountSelector":"687","amount":10,"reference":"Reference123","destination":{"destinationType":"toAccount","accountType":"SCAN","holderName":"John Doe","accountNumber":"11111111","sortCode":"111111","iban":null}}As a curl command:
curl -X POST https://api.volume.com/api/payouts \
-H "Content-Type: application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json" \
-H "X-Application-Id: merchant-app-123" \
-H "X-Application-Secret: merchant-app-secret123" \
-d '{"applicationId":"merchant-app-123","payInAccountSelector":"687","amount":10,"reference":"Reference123","destination":{"destinationType":"toAccount","accountType":"SCAN","holderName":"John Doe","accountNumber":"11111111","sortCode":"111111","iban":null}}'What Gets Signed: Component Mapping
The Volume API requires you to sign these components in this exact order:
| Required Order | What You Have in Your Request | Plain English | RFC 9421 Name | Value from Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HTTP method (POST, GET, etc.) | Request method | @method | POST |
| 2 | URL path including query string | Request path | @path | /api/payouts |
| 3 | Host header | Domain/authority | @authority | api.volume.com |
| 4 | Content-Digest header (from Step 1) | SHA-512 body hash | content-digest | sha-512=:mEWXIS7M...==: |
| 5 | Content-Type header | Media type | content-type | application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json |
| 6 | Content-Length header | Body size in bytes | content-length | 40 |
| 7 | X-Application-Id header | Your application ID | (custom header) | merchant-app-123 |
| 8 | X-Application-Secret header | Your application Secret | (custom header) | merchant-app-secret123 |
| 9 | Signature metadata (timestamp, keyid, alg, nonce) | Signature parameters | @signature-params | ("@method" "@path"...);created=...;keyid=... |
Understanding the naming:
@prefix = "Derived component" (extracted from request line, not headers)- No
@prefix = Standard HTTP header - RFC 9421 terminology: "Covered components" just means "the list of request parts included in the signature"
Important rules:
@methodmust be UPPERCASE (POST, GET, DELETE, etc.)@pathmust include query string if present (e.g.,/api/payouts?status=PENDING)@authorityis the host, omitting default ports 80 and 443, but including any other port (e.g.,api.volume.comorapi.volume.com:8080)- Header names are lowercase in the signature base
- Missing headers use empty string value
"" - Component order is fixed and cannot be changed
Build the Signature Base String
Now format these components into the signature base string that you'll sign:
Signature Base Format:
"component-name": value
"component-name": value
...
"@signature-params": (component list);created=timestamp;keyid="key-id";alg="ed25519";nonce="nonce-value"For our example request:
"@method": POST
"@path": /api/payouts
"@authority": api.volume.com
"content-digest": sha-512=:BQeizl2zZ3ym43S/F/76zbzTI9nHH5lyOAsQJvzgJz2DokNVvdyhaa20jcMzEppZf+hG1/tlzSfnUrJAnbCgCQ==:
"content-type": application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
"content-length": 40
"x-application-id": merchant-app-123
"x-application-secret": merchant-app-secret123
"@signature-params": ("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"Construction rules:
-
For each component (in order):
- Component name in double quotes
- Colon character followed by one space character (written as colon+space or ": ")
- Component value (NOT quoted)
- Newline character (
\n)
-
Last line is special -
"@signature-params":- Contains the parenthesized list of all component names
- Followed by signature metadata:
created,keyid,alg,nonce - Format:
"@signature-params": (COMPONENTS);created=TIMESTAMP;keyid="KEY_ID";alg="ed25519";nonce="NONCE"
Where signature parameters come from:
created= Current Unix timestamp in seconds (e.g.,1735660800)keyid= Your key identifier provided by Volume (e.g.,"merchant-key-123")alg= Always"ed25519"for this APInonce= Random unique value (REQUIRED) - use UUID4 or similar cryptographically random string (max 50 characters)
⚠️ CRITICAL: The content-digest value in the signature base MUST match the Content-Digest header calculated from the EXACT body bytes you send. The body used for digest calculation, signature base construction, and the actual HTTP request body MUST be byte-for-byte identical - same formatting, same serialization, no extra spaces or newlines. Any difference will cause verification to fail.
Special Case: GET Requests (No Body)
For GET or DELETE requests without a body:
Example request:
GET /api/payouts/12345 HTTP/1.1
Host: api.volume.com
X-Application-Id: merchant-app-123
X-Application-Secret: merchant-app-secret123Signature base:
"@method": GET
"@path": /api/payouts/12345
"@authority": api.volume.com
"content-digest": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"content-type": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"content-length": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"x-application-id": merchant-app-123
"x-application-secret": merchant-app-secret123
"@signature-params": ("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660900;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="b2c3d4e5-f6a7-48b9-c0d1-e2f3a4b5c6d7"Note: The components content-digest, content-type, and content-length still appear in the signature base with empty values (nothing after colon+space). This maintains consistent signature structure.
Step 3: Sign the Signature Base
- Convert signature base string to UTF-8 bytes
- Sign bytes using Ed25519 with your private key
- Encode signature as base64
Pseudocode:
signatureBaseBytes = signatureBase.toBytes(UTF-8)
signatureBytes = ed25519Sign(privateKey, signatureBaseBytes)
signatureBase64 = base64Encode(signatureBytes)Result: 64-byte Ed25519 signature → 88-character base64 string
Step 4: Build Signature-Input Header
Format: sig1=(COMPONENTS);created=TIMESTAMP;keyid="KEY_ID";alg="ed25519";nonce="NONCE"
Template:
sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="your-key-id";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"Components:
sig1= Signature label (always "sig1")(...)= Parentheses containing space-separated quoted component namescreated= Unix timestamp (seconds)keyid= Your key identifier (quoted)alg= Algorithm name (always "ed25519", quoted)nonce= Random unique value (quoted) - REQUIRED - use UUID4 or similar
Example:
Signature-Input: sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"Step 5: Build Signature Header
Format: sig1=:BASE64_SIGNATURE:
Template:
sig1=:base64signature:The signature value is wrapped in colons (:) per RFC 8941 Byte Sequence format.
Example:
Signature: sig1=:k9Uf2vMr8pL3nQ5wX7yZ1A==:Step 6: Add Headers to Request
Add these three headers to your HTTP request:
Content-Digest: sha-512=:base64hash:
Signature-Input: sig1=(...);created=...;keyid="...";alg="ed25519";nonce="..."
Signature: sig1=:base64signature:Send the request with all original headers plus these signature headers.
Complete Example
Request Details
Method: POST
URL: https://api.volume.com/api/payouts
Headers:
Content-Type: application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
X-Application-Id: merchant-app-123
X-Application-Secret: merchant-app-123
Body: {"applicationId":"merchant-app-123","payInAccountSelector":"687","amount":10,"reference":"Reference123","destination":{"destinationType":"toAccount","accountType":"SCAN","holderName":"John Doe","accountNumber":"11111111","sortCode":"111111","iban":null}}Step 1: Content Digest
Body bytes: {"applicationId":"merchant-app-123","payInAccountSelector":"687","amount":10,"reference":"Reference123","destination":{"destinationType":"toAccount","accountType":"SCAN","holderName":"John Doe","accountNumber":"11111111","sortCode":"111111","iban":null}}
SHA-512 hash (hex): 0507A2CE5DB3677CA6E374BF17FEFACDBCD323D9C71F9972380B1026FCE0273D83A24355BDDCA169ADB48DC333129A597FE846D7FB65CD27E752B2409DB0A009
Base64: BQeizl2zZ3ym43S/F/76zbzTI9nHH5lyOAsQJvzgJz2DokNVvdyhaa20jcMzEppZf+hG1/tlzSfnUrJAnbCgCQ==
Content-Digest: sha-512=:BQeizl2zZ3ym43S/F/76zbzTI9nHH5lyOAsQJvzgJz2DokNVvdyhaa20jcMzEppZf+hG1/tlzSfnUrJAnbCgCQ==:Step 2: Covered Components
@method
@path
@authority
content-digest
content-type
content-length
x-application-id
x-application-secretStep 3: Component Values
@method = POST
@path = /api/payouts
@authority = api.volume.com
content-digest = sha-512=:BQeizl2zZ3ym43S/F/76zbzTI9nHH5lyOAsQJvzgJz2DokNVvdyhaa20jcMzEppZf+hG1/tlzSfnUrJAnbCgCQ==:
content-type = application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
content-length = 40
x-application-id = merchant-app-123
x-application-secret = merchant-app-secret123Step 4: Signature Base
"@method": POST
"@path": /api/payouts
"@authority": api.volume.com
"content-digest": sha-512=:BQeizl2zZ3ym43S/F/76zbzTI9nHH5lyOAsQJvzgJz2DokNVvdyhaa20jcMzEppZf+hG1/tlzSfnUrJAnbCgCQ==:
"content-type": application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
"content-length": 40
"x-application-id": merchant-app-123
"x-application-secret": merchant-app-secret123
"@signature-params": ("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"Step 5: Sign
Signature base → UTF-8 bytes → Ed25519 sign → Base64
Result: k9Uf2vMr8pL3nQ5wX7yZ1A2bC4dE6fG8hI0jK2lM4nO6pQ8rS0tU2vW4xY6zA==Step 6-7: Headers
Signature-Input: sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"
Signature: sig1=:k9Uf2vMr8pL3nQ5wX7yZ1A2bC4dE6fG8hI0jK2lM4nO6pQ8rS0tU2vW4xY6zA==:Step 8: Final Request
POST /api/payouts HTTP/1.1
Host: api.volume.com
Content-Type: application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
Content-Length: 40
X-Application-Id: merchant-app-123
X-Application-Secret": merchant-app-secret123
Content-Digest: sha-512=:mEWXIS7MaLRuGgxOBdODa3xqM7XOexkQ7/TDUa6qAaynBPnPxNPnLx4zQ8U2MzOz5vkA5zL5R9GuzFO43JDcvw==:
Signature-Input: sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"
Signature: sig1=:k9Uf2vMr8pL3nQ5wX7yZ1A2bC4dE6fG8hI0jK2lM4nO6pQ8rS0tU2vW4xY6zA==:
{"amount":"100.00","currency":"GBP"}Complete Example: GET Request (No Body)
Request Details
Method: GET
URL: https://api.volume.com/api/payouts/12345
Headers:
X-Application-Id: merchant-app-123
X-Application-Secret: merchant-app-secret123
Body: (none)Step 1: Content Digest
No body → Skip Content-Digest header calculation
DO NOT add Content-Digest header to the requestStep 2-3: Component Values
@method = GET
@path = /api/payouts/12345
@authority = api.volume.com
content-digest = (empty string "")
content-type = (empty string "")
content-length = (empty string "")
x-application-id = merchant-app-123
x-application-secret = merchant-app-secret123Step 4: Signature Base
"@method": GET
"@path": /api/payouts/12345
"@authority": api.volume.com
"content-digest": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"content-type": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"content-length": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"x-application-id": merchant-app-123
"x-application-secret": merchant-app-secret123
"@signature-params": ("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660900;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="b2c3d4e5-f6a7-48b9-c0d1-e2f3a4b5c6d7"Note: The content-digest, content-type, and content-length lines have empty values (nothing after the colon+space). This is intentional and maintains consistent signature structure.
Step 5-7: Sign and Build Headers
Signature-Input: sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660900;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="b2c3d4e5-f6a7-48b9-c0d1-e2f3a4b5c6d7"
Signature: sig1=:xY6zA1B2cD3eF4gH5iJ6kL7mN8oP9qR0sT1uV2wX3yZ4aB5cD6eF7gH8iJ9kL0m==:Step 8: Final GET Request
GET /api/payouts/12345 HTTP/1.1
Host: api.volume.com
X-Application-Id: merchant-app-123
"x-application-secret": merchant-app-secret123
Signature-Input: sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660900;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="b2c3d4e5-f6a7-48b9-c0d1-e2f3a4b5c6d7"
Signature: sig1=:xY6zA1B2cD3eF4gH5iJ6kL7mN8oP9qR0sT1uV2wX3yZ4aB5cD6eF7gH8iJ9kL0m==:Important: Notice there is NO Content-Digest header in the final request, even though content-digest appears in the Signature-Input metadata and signature base with an empty value.
Understanding Your Private Key
What You'll Receive
Volume will provide you with an Ed25519 private key in one of these formats:
Option 1: PEM Format (most common)
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
MC4CAQAwBQYDK2VwBCIEIJ1hsZ3v/Vpguohk9JLsLMRESMVpezJpGXA7rAMcrn9g
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----Option 2: Raw Base64 Format
nWGxne/9WmC6hEr0kuwsxERJxWl7MmkZcDusAxyuf2A=What is PEM Format?
PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) is a standard container format for cryptographic keys. It wraps your key in a text format with:
- Header line:
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- - Base64-encoded key data (may span multiple lines)
- Footer line:
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
The PEM format includes metadata about the key type. For Ed25519 keys, the actual 32-byte key is embedded inside this structure.
How to Extract Your Key
If you receive a PEM-formatted key, you need to extract the raw 32-byte Ed25519 key:
Using OpenSSL (Command Line)
# If your key is in a file (e.g., private_key.pem)
openssl pkey -in private_key.pem -outform DER | tail -c 32 | base64
# This extracts the last 32 bytes (your Ed25519 seed) and encodes it as base64Using Code (Examples)
Python:
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization
with open("private_key.pem", "rb") as f:
pem_data = f.read()
private_key = serialization.load_pem_private_key(pem_data, password=None)
raw_key = private_key.private_bytes(
encoding=serialization.Encoding.Raw,
format=serialization.PrivateFormat.Raw,
encryption_algorithm=serialization.NoEncryption()
)
import base64
key_base64 = base64.b64encode(raw_key).decode('ascii')
print(key_base64) # This is what you use for signingNode.js:
const crypto = require('crypto');
const fs = require('fs');
const pemKey = fs.readFileSync('private_key.pem', 'utf8');
const keyObject = crypto.createPrivateKey(pemKey);
// Export as raw key material
const rawKey = keyObject.export({
type: 'pkcs8',
format: 'der'
});
// Ed25519 private key is the last 32 bytes
const ed25519Key = rawKey.slice(-32);
const keyBase64 = ed25519Key.toString('base64');
console.log(keyBase64); // This is what you use for signingJava/Kotlin:
import java.security.KeyFactory
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec
import java.util.Base64
fun extractEd25519Key(pemContent: String): String {
// Remove PEM headers and newlines
val base64Key = pemContent
.replace("-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----", "")
.replace("-----END PRIVATE KEY-----", "")
.replace("\\s".toRegex(), "")
// Decode the PKCS#8 structure
val pkcs8Bytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Key)
// Ed25519 private key is the last 32 bytes
val ed25519Key = pkcs8Bytes.takeLast(32).toByteArray()
// Encode as base64
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(ed25519Key)
}Where You Use the Key
The private key is used in Step 3 of the signing process:
Step 2: Build Signature Base
↓
Step 3: Sign the Signature Base ← YOU USE YOUR PRIVATE KEY HERE
↓
Step 4: Build Signature-Input HeaderYour Ed25519 signing library will need the raw 32-byte key (either as bytes or base64-encoded, depending on the library).
Key Storage Best Practices
-
Never hardcode keys - Use environment variables or secrets management
-
Never commit keys to git - Add
*.pemand key files to.gitignore -
Restrict file permissions -
chmod 600 private_key.pemon Unix systems -
Use environment variables:
export VOLUME_PRIVATE_KEY="nWGxne/9WmC6hEr0kuwsxERJxWl7MmkZcDusAxyuf2A=" export VOLUME_KEY_ID="your-key-id" export VOLUME_APPLICATION_ID="your-app-id" -
Use secrets managers in production:
- AWS Secrets Manager
- Google Cloud Secret Manager
- Azure Key Vault
- HashiCorp Vault
Verification (Server Side)
The Volume API server performs these steps:
- Extract signature headers from request
- Parse Signature-Input to get: covered components, timestamp, keyId, algorithm, nonce
- Validate timestamp:
now - created ≤ 300 seconds(5 minutes) - Validate nonce: Check nonce is present and not previously used (replay attack prevention)
- Validate x-application-id: Check header is present and valid
- Validate x-application-secret: Check header is present and valid
- Resolve public key using keyId and applicationId
- Verify Content-Digest matches request body (if present)
- Reconstruct signature base from request components (including nonce in @signature-params)
- Verify signature using Ed25519 with public key
- Record nonce to prevent reuse
- Accept or reject request based on verification result
Security Considerations
Signature Expiration
- Signatures are valid for 5 minutes (300 seconds) from creation
- Use current timestamp when signing:
created = currentTimeSeconds() - Expired signatures are rejected to prevent replay attacks
Replay Attack Protection
The created timestamp provides basic replay protection with a 5-minute window. Additionally, a nonce parameter is REQUIRED for all requests to prevent replay attacks:
"@signature-params": (...);created=1735660800;keyid="key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="unique-random-value"The server tracks used nonces within the validity window and rejects duplicate nonces. Per RFC 9421 Section 2.3, nonce is defined as "a random unique value generated for this signature as a String value." Use UUID4 or a similar cryptographically random string.
Key Security
- Never expose private key in logs, configs, or version control
- Store private key securely (environment variables, secrets manager, HSM)
- Use unique keyId for each key pair
- Rotate keys periodically (recommended: every 12 months)
Clock Synchronization
- Ensure your server clock is synchronized (use NTP)
- Clock skew >5 minutes will cause signature failures
HTTPS Required
- Always use HTTPS (not HTTP)
- Signatures prove integrity, not confidentiality
- TLS encrypts the request, signatures verify it hasn't been tampered with
References
- RFC 9421: HTTP Message Signatures - https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc9421.html (opens in a new tab)
- RFC 9530: Digest Fields - https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc9530.html (opens in a new tab)
- RFC 8032: Edwards-Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (EdDSA) - https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc8032.html (opens in a new tab)
- RFC 8941: Structured Field Values for HTTP - https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc8941.html (opens in a new tab)
Appendix: Component Extraction Rules
Derived Components
| Component | Extraction Rule |
|---|---|
@method | HTTP method in uppercase (e.g., GET, POST) |
@path | Request URI path + query string (e.g., /api/payouts?status=PENDING) |
@authority | Host header value or request host (e.g., api.volume.com) |
Header Components
- Extract from HTTP request headers
- Header names are case-insensitive during lookup
- Store in lowercase in signature base
- Missing headers default to empty value (nothing after colon+space)
Special Cases
Query Parameters:
- Include in
@path:/api/payouts?status=PENDING&limit=10 - Do NOT separate or encode differently
Port Numbers:
- Omit standard ports (80, 443)
- Include non-standard ports:
api.volume.com:8080
Empty Body (GET, DELETE requests):
- Do NOT send
Content-Digestheader in the HTTP request - BUT you MUST still include
content-digestas a component in the signature base with an empty value (nothing after colon+space) - Set
content-length: 0or omitcontent-lengthheader - Example signature base line:
"content-digest":(nothing after colon+space)
Header Order:
- Components must appear in the exact order listed in Step 2
- Order affects signature validity
Test Vectors
Vector 1: POST Request (matches Complete Example)
Input:
Method: POST
Path: /api/payouts
Host: api.volume.com
Body: {"amount":"100.00","currency":"GBP"}
Content-Type: application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
Timestamp: 1735660800
KeyId: merchant-key-123
ApplicationId: merchant-app-123
Nonce: 550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000Expected Signature Base:
"@method": POST
"@path": /api/payouts
"@authority": api.volume.com
"content-digest": sha-512=:mEWXIS7MaLRuGgxOBdODa3xqM7XOexkQ7/TDUa6qAaynBPnPxNPnLx4zQ8U2MzOz5vkA5zL5R9GuzFO43JDcvw==:
"content-type": application/vnd.volume.v1.0+json
"content-length": 40
"x-application-id": merchant-app-123
"x-application-secret": merchant-app-secret123
"@signature-params": ("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"Expected Signature-Input Header:
sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660800;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"Vector 2: GET Request (matches Complete Example)
Input:
Method: GET
Path: /api/payouts/12345
Host: api.volume.com
Body: (none)
Timestamp: 1735660900
KeyId: merchant-key-123
ApplicationId: merchant-app-123
Nonce: b2c3d4e5-f6a7-48b9-c0d1-e2f3a4b5c6d7Expected Signature Base:
"@method": GET
"@path": /api/payouts/12345
"@authority": api.volume.com
"content-digest": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"content-type": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"content-length": ← (one space after colon, then newline - no value)
"x-application-id": merchant-app-123
"x-application-secret": merchant-app-secret123
"@signature-params": ("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660900;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="b2c3d4e5-f6a7-48b9-c0d1-e2f3a4b5c6d7"Expected Signature-Input Header:
sig1=("@method" "@path" "@authority" "content-digest" "content-type" "content-length" "x-application-id" "x-application-secret");created=1735660900;keyid="merchant-key-123";alg="ed25519";nonce="b2c3d4e5-f6a7-48b9-c0d1-e2f3a4b5c6d7"Note: These test vectors match the Complete Example sections exactly. You can use these values to verify your implementation produces the same signature base and headers.